What is over-clocking?
Since clock doubling and bus speed can be freely adjusted on the motherboard according to your desires, you can in
principle make the CPU run at 300 MHz. You set the bus to 75 MHz and the clock factor to 4. Then the CPU runs at 300
MHz – if it runs. The question is whether the chip will tolerate that - if it will give a stable performance, since clock doubling
means more than added heat.
We have now seen that there are two frequencies which can be manipulated, if you want to re-clock the CPU:
l The bus frequency can be increased, let's say from 66 to 75 MHz.
The CPU frequency can be increased. That can happen as a result of an increased bus speed, which also affects
the CPU frequency, or it can happen by using a greater clock factor. Or it can happen through a combination of both
techniques.
l
Both techniques result in a faster PC. If the bus frequency is increased, it affects all data transport to and from RAM. It will
work faster, to the joy of all work done on the PC. When the CPU internal frequency is increased, many applications will be happily affected.
Cooling
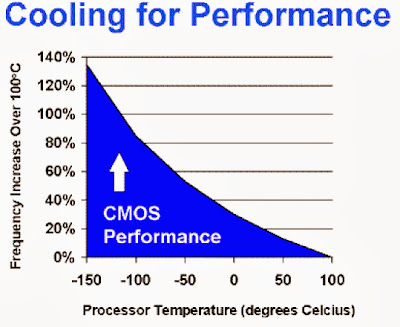
The tuning will often work, but it requires good cooling of the CPU, the more cooling the higher you can have the clock
frequency. CPU's are built in CMOS technology. That is a type chip which works better the cooler it is. See this relationship
between temperature and performance:
This form of cooling is extreme, but it works. Kryotech can make a standard CPU work at 400-700 MHz! But is requires that it
is kept constantly cooled to -40 degree F.
Since clock doubling and bus speed can be freely adjusted on the motherboard according to your desires, you can in
principle make the CPU run at 300 MHz. You set the bus to 75 MHz and the clock factor to 4. Then the CPU runs at 300
MHz – if it runs. The question is whether the chip will tolerate that - if it will give a stable performance, since clock doubling
means more than added heat.
We have now seen that there are two frequencies which can be manipulated, if you want to re-clock the CPU:
l The bus frequency can be increased, let's say from 66 to 75 MHz.
The CPU frequency can be increased. That can happen as a result of an increased bus speed, which also affects
the CPU frequency, or it can happen by using a greater clock factor. Or it can happen through a combination of both
techniques.
l
Both techniques result in a faster PC. If the bus frequency is increased, it affects all data transport to and from RAM. It will
work faster, to the joy of all work done on the PC. When the CPU internal frequency is increased, many applications will be happily affected.
Cooling
The tuning will often work, but it requires good cooling of the CPU, the more cooling the higher you can have the clock
frequency. CPU's are built in CMOS technology. That is a type chip which works better the cooler it is. See this relationship
between temperature and performance:
 |
| It is fed from the compressor in the bottom of the cabinet: |
This form of cooling is extreme, but it works. Kryotech can make a standard CPU work at 400-700 MHz! But is requires that it
is kept constantly cooled to -40 degree F.

No comments:
Post a Comment